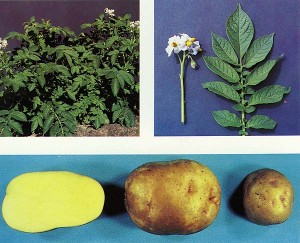
Yukon Gold (Solanum tuberosum)
ORIGIN: Released jointly by Agriculture Canada and the University of Guelph, Guelph, Ontario, Canada in 1981. Yukon Gold was selected from a cross between W5279-4 (a yellow-fleshed diploid hybrid of Solanum phureja and haploid cv Katahdin) and Norgleam. It was tested under the pedigree G6666-4Y.
CHARACTERISTICS: Yukon Gold has medium-early maturity (late in the mid-Atlantic Region of the U.S.), moderate yields, moderate specific gravity and relatively attractive tuber type. Plants are medium-large to large and upright. Stems are purplish but are more green in the upper portion of the plant. Leaf petioles extend downward. Nodes are not swollen. Leaves have a distinct terminal leaflet with four pairs of primary leaflets which are largest near the terminal leaflet. Secondary leaflets vary from two on lower leaves to 6-8 on upper leaves, usually in pairs. The number of tertiary leaves also increases from lower to upper leaves. Flowers are violet to light-violet with yellow anthers. Tubers slightly oval, may be somewhat flattened with yellow-white skin and light yellow tuber flesh. Its shallow, pink eyes distinguish Yukon Gold from other yellow-skinned, yellow-fleshed cultivars.
STRENGTHS & WEAKNESSES: Yukon Gold is resistant to mild mosaic, moderately resistant to leafroll virus and susceptible to virus Y, common scab and air pollution. In some growing areas, hollow heart and internal heat necrosis may be a problem. Yukon Gold retains the yellow flesh color when baked, boiled or french-fried. The attractive tubers are well suited for fresh marketing. Plant establishment is irregular, particularly from basal seed pieces. Pre-cut or whole seed is used in some areas to improve plant stands.